Basics of Computer Networking
 Computer Networking is the practice of connecting computers together to enable communication and data exchange between them. In general, Computer Network is a collection of two or more computers. It helps users to communicate more easily. In this article, we are going to discuss the basics which everyone must know before going deep into Computer Networking.
Computer Networking is the practice of connecting computers together to enable communication and data exchange between them. In general, Computer Network is a collection of two or more computers. It helps users to communicate more easily. In this article, we are going to discuss the basics which everyone must know before going deep into Computer Networking.
How Does a Computer Network Work?
Basics building blocks of a Computer network are Nodes and Links. A Network Node can be illustrated as Equipment for Data Communication like a Modem, Router, etc., or Equipment of a Data Terminal like connecting two computers or more. Link in Computer Networks can be defined as wires or cables or free space of wireless networks. The working of Computer Networks can be simply defined as rules or protocols which help in sending and receiving data via the links which allow Computer networks to communicate. Each device has an IP Address, that helps in identifying a device.Basic Terminologies of Computer Networks
- Network: A network is a collection of computers and devices that are connected together to enable communication and data exchange.
- Nodes: Nodes are devices that are connected to a network. These can include computers, Servers, Printers, Routers Switches, and other devices.
- Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules and standards that govern how data is transmitted over a network. Examples of protocols include TCP/IP, HTTP, and FTP
- Topology: Network topology refers to the physical and logical arrangement of nodes on a network. The common network topologies include bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree.
- Service Provider Networks: These types of Networks give permission to take Network Capacity and Functionality on lease from the Provider. Service Provider Networks include Wireless Communications, Data Carriers, etc.
- IP Address: An IP address is a unique numerical identifier that is assigned to every device on a network. IP addresses are used to identify devices and enable communication between them.
- DNS: The Domain Name System (DNS) is a protocol that is used to translate human-readable domain names (such as www.google.com) into IP addresses that computers can understand.
- Firewall: A firewall is a security device that is used to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls are used to protect networks from unauthorized access and other security threats.
Types of Enterprise Computer Networks
- LAN: A Local Area Network(LAN) is a network that covers a small area, such as an office or a home. LANs are typically used to connect computers and other devices within a building or a campus.
- WAN: A Wide Area Network(WAN) is a network that covers a large geographic area, such as a city, country, or even the entire world. WANs are used to connect LANs together and are typically used for long-distance communication.
- Cloud Networks: Cloud Networks can be visualized with a Wide Area Network (WAN) as they can be hosted on public or private cloud service providers and cloud networks are available if there is a demand. Cloud Networks consist of Virtual Routers, Firewalls, etc.
- Open system: A system that is connected to the network and is ready for communication.
- Closed system: A system that is not connected to the network and can’t be communicated with.
Types of Computer Network Architecture
Computer Network falls under these broad Categories:- Client-Server Architecture: Client-Server Architecture is a type of Computer Network Architecture in which Nodes can be Servers or Clients. Here, the server node can manage the Client Node Behaviour.
- Peer-to-Peer Architecture: InP2P (Peer-to-Peer) Architecture, there is not any concept of a Central Server. Each device is free for working as either client or server.
Network Devices
An interconnection of multiple devices, also known as hosts, that are connected using multiple paths for the purpose of sending/receiving data or media. Computer networks can also include multiple devices/mediums which help in the communication between two different devices; these are known as Network Devices and include things such as routers, switches, hubs, and bridges.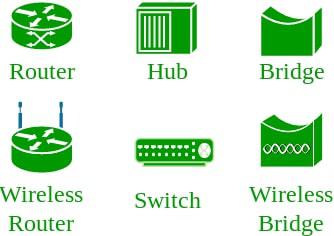
Network Devices
Network Topology
The Network Topology is the layout arrangement of the different devices in a network. Common examples include Bus, Star, Mesh, Ring, and Daisy chain.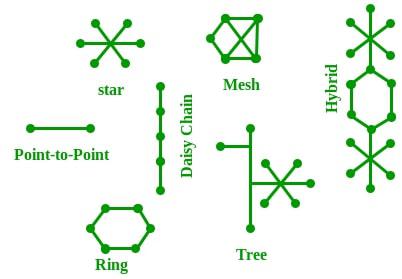
Network Topology
OSI Model
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection . It is a reference model that specifies standards for communications protocols and also the functionalities of each layer. The OSI has been developed by the International Organization For Standardization and it is 7 layer architecture. Each layer of OSI has different functions and each layer has to follow different protocols. The 7 layers are as follows:- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session layer
- Presentation layer
- Application Layer
Protocol
A protocol is a set of rules or algorithms which define the way how two entities can communicate across the network and there exists a different protocol defined at each layer of the OSI model. A few such protocols are TCP, IP, UDP, ARP, DHCP, FTP, and so on.Unique Identifiers of Network
Hostname: Each device in the network is associated with a unique device name known as Hostname. Type “hostname” in the command prompt(Administrator Mode) and press ‘Enter’, this displays the hostname of your machine.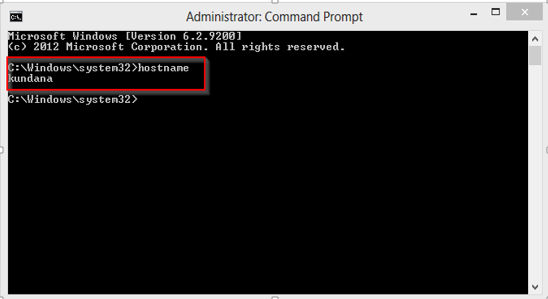
HostName
| Port Types | Range |
|---|---|
| Well known Ports | 0 – 1023 |
| Registered Ports | 1024 – 49151 |
| Ephemeral Ports | 49152 – 65535 |
List of Ports
Other Related Concepts
DNS Server: DNS stands for Domain Name System. DNS is basically a server that translates web addresses or URLs (ex: www.google.com) into their corresponding IP addresses. We don’t have to remember all the IP addresses of each and every website. The command ‘nslookup’ gives you the IP address of the domain you are looking for. This also provides information on our DNS Server. \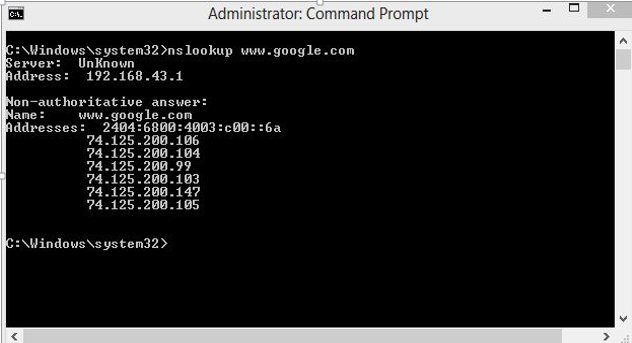
Domain IP Address
Choose Certified Systems as your perfect GATE 2025 Preparation partner with these newly launched programs and any IT solutions.
Comments
Post a Comment